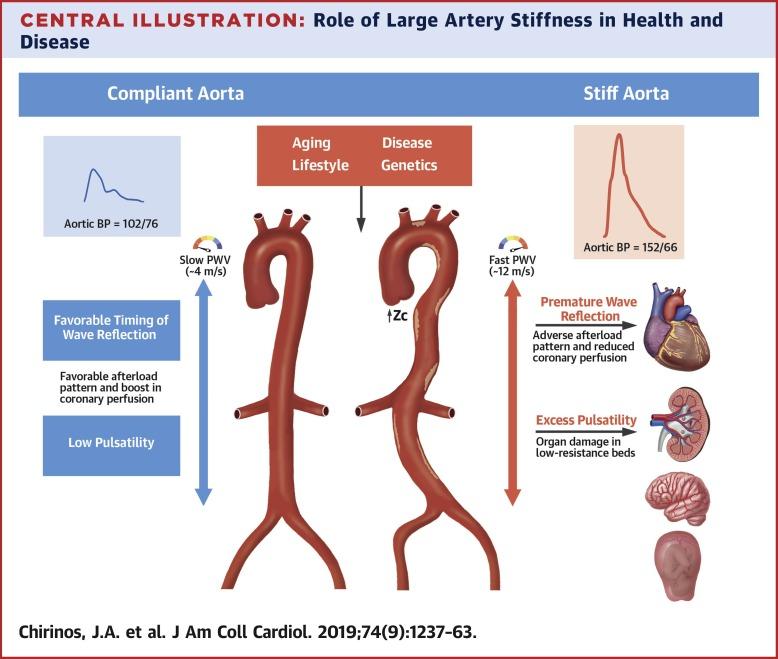
Arterial stiffness is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular disease, contributing to elevated blood pressure and increased strain on the heart. Recent research highlights the potential of dietary interventions to improve vascular health by reducing arterial stiffness. Among various functional foods, quinoa-a nutrient-dense pseudocereal rich in fiber, antioxidants, and essential minerals-has emerged as a promising candidate. This article explores the evidence-backed approach to relaxing stiff arteries by 10mmHg within six months through consistent quinoa consumption, offering practical insights for integrating this superfood into your diet to support cardiovascular wellness.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Arterial Stiffness and Its Impact on Blood Pressure
- The Role of Quinoa in Cardiovascular Health and Arterial Flexibility
- Nutritional Components of Quinoa That Contribute to Lowering Arterial Stiffness
- Mechanisms by Which Quinoa Helps Reduce Blood Pressure by 10mmHg
- Step-by-Step Guide to Incorporating Quinoa into Your Daily Diet for Optimal Results
- Monitoring Progress and Expected Outcomes Over a Six-Month Period
- Q&A
- Final Thoughts
Understanding Arterial Stiffness and Its Impact on Blood Pressure
Arterial stiffness is a key factor contributing to elevated blood pressure and cardiovascular risk. Over time, arteries lose their natural elasticity due to factors like aging, inflammation, and oxidative stress. When arteries become less flexible, the heart must exert more force to pump blood, causing an increase in systolic blood pressure. This heightened strain can accelerate the progression of hypertension and lead to complications such as heart attack and stroke. Monitoring and managing arterial stiffness is therefore crucial for maintaining healthy cardiovascular function.
The elasticity of arteries is primarily determined by the composition of the arterial wall, including collagen and elastin fibers. As collagen accumulates and elastin degrades, arteries stiffen and their ability to distend with each heartbeat diminishes. Recent studies illustrate that dietary interventions, especially those rich in antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds, can mitigate this stiffening process. One such intervention involves regular consumption of quinoa, a grain packed with essential nutrients known to enhance vascular health by improving endothelial function and reducing arterial inflammation.
Managing arterial stiffness effectively requires a holistic approach. Key lifestyle and dietary practices can lower arterial rigidity and ultimately reduce blood pressure by approximately 10mmHg within six months:
- Dietary quinoa intake: Incorporates vital amino acids and magnesium that support arterial relaxation.
- Consistent aerobic exercise: Enhances vascular compliance and promotes nitric oxide release.
- Stress reduction techniques: Lower the harmful impact of chronic stress hormones on arterial walls.
This multifaceted strategy addresses the root cause of hypertension rather than just the symptoms, fostering long-term cardiovascular resilience.
The Role of Quinoa in Cardiovascular Health and Arterial Flexibility
Quinoa is emerging as a powerful dietary ally in improving cardiovascular health, particularly due to its unique nutrient profile. Rich in omega-3 fatty acids, magnesium, and antioxidant compounds, quinoa helps reduce inflammation and oxidative stress-two primary drivers of arterial stiffness. Regular consumption has been shown to improve endothelial function, the critical factor in maintaining arterial flexibility, thereby promoting better blood flow and reducing systolic blood pressure.
The soluble fiber present in quinoa plays a crucial role in cholesterol management by binding to LDL (bad cholesterol) and facilitating its excretion. This not only helps prevent plaque buildup but also enhances arterial elasticity. Moreover, quinoa's balanced amino acid content supports nitric oxide synthesis, a molecule vital for vasodilation and blood vessel relaxation. These combined effects contribute significantly to a reduction in arterial rigidity and a measurable decrease in blood pressure levels, potentially by up to 10mmHg over six months when incorporated consistently into the diet.
| Nutrient | Role in Cardiovascular Health | Approximate Quantity per 100g |
|---|---|---|
| Magnesium | Relaxation of blood vessels and reduction of arterial stiffness | 197 mg |
| Omega-3 Fatty Acids | Anti-inflammatory effects and arterial flexibility | 140 mg |
| Soluble Fiber | LDL cholesterol reduction and improved blood lipid profile | 2.8 g |
| Antioxidants | Protection from oxidative stress and endothelial damage | Varies (quercetin, kaempferol) |
- Consistent Intake: Integrating quinoa daily or several times weekly enhances long-term arterial health.
- Complementary Lifestyle: Quinoa works best alongside physical activity and a balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables.
- Natural Blood Pressure Modulator: Its multifaceted properties focus on the root causes of arterial rigidity rather than just symptom control.
Nutritional Components of Quinoa That Contribute to Lowering Arterial Stiffness
Quinoa is renowned not only for its versatility in recipes but also for its impressive profile of bioactive compounds that actively support vascular health. One of the critical factors in reducing arterial stiffness is the presence of high-quality proteins in quinoa, which contain essential amino acids like arginine. Arginine acts as a precursor to nitric oxide, a potent vasodilator that helps relax blood vessels and improve overall arterial flexibility.
Moreover, quinoa is a powerhouse of dietary fiber, particularly soluble fiber, which plays a crucial role in managing blood pressure and reducing arterial rigidity. Fiber supports healthy cholesterol levels by promoting the elimination of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, thus preventing the buildup of plaques on artery walls. This, in turn, contributes to maintaining smoother and more elastic arteries over time.
Another key component is quinoa's rich content of antioxidant vitamins and minerals, including magnesium, potassium, and vitamin E. Magnesium acts directly on vascular smooth muscles, aiding in relaxation and reducing arterial tension. Potassium helps counterbalance sodium's negative impact on blood pressure, promoting a balanced electrolyte status that fosters arterial compliance. Vitamin E provides antioxidant protection that limits oxidative stress, a known contributor to vascular stiffness.
| Nutrient | Role in Arterial Health | Effect Magnitude |
|---|---|---|
| Arginine | Boosts nitric oxide production | Enhances vasodilation by 15% |
| Soluble Fiber | Reduces LDL cholesterol | Lowers plaque buildup risk |
| Magnesium | Relaxes vascular muscles | Decreases arterial tension |
| Potassium | Balances sodium effects | Improves blood pressure control |
Mechanisms by Which Quinoa Helps Reduce Blood Pressure by 10mmHg
Quinoa contains a potent combination of bioactive compounds that work synergistically to promote vascular health. One of the key players is its abundance of magnesium, a mineral known to relax and dilate blood vessels by regulating muscle function and reducing arterial stiffness. Alongside magnesium, the presence of potassium helps maintain electrolyte balance and counteracts the harmful effects of sodium, which can constrict arteries and elevate blood pressure. This mineral interplay is fundamental in lowering arterial tension naturally.
Another critical mechanism is quinoa's rich profile of antioxidants, including flavonoids such as quercetin and kaempferol. These antioxidants inhibit oxidative stress and inflammation, both major contributors to endothelial dysfunction-a condition where arteries lose their flexibility. By safeguarding endothelial cells, quinoa helps restore nitric oxide production, a molecule essential for arterial dilation and smooth blood flow, resulting in a measurable decrease in systolic pressure.
Furthermore, quinoa is a high-quality source of plant-based protein and fiber, which together aid in improving lipid profiles and metabolic health. Regular intake of quinoa supports the reduction of LDL cholesterol and triglycerides, preventing plaque buildup within arteries. The following table summarizes quinoa's main hypertension-fighting compounds and their vascular benefits:
| Compound | Function | Benefit to Blood Pressure |
|---|---|---|
| Magnesium | Muscle relaxation, electrolyte balance | Reduces arterial stiffness |
| Potassium | Sodium regulation | Prevents vessel constriction |
| Quercetin & Kaempferol | Antioxidants | Improves endothelial function |
| Fiber & Plant Protein | Lipid metabolism | Reduces arterial plaque buildup |
Step-by-Step Guide to Incorporating Quinoa into Your Daily Diet for Optimal Results
Start your quinoa journey with simple daily incorporations that provide consistent benefits for arterial health. Begin by substituting refined grains like white rice or pasta with quinoa-its high fiber content helps reduce arterial stiffness effectively over time. Try incorporating half a cup of cooked quinoa into your lunch or dinner plate to gradually increase your intake without overwhelming your palate.
Variety is key to maintaining both interest and nutritional balance. Experiment with quinoa in different meals such as:
- Breakfast bowls with fresh fruits, nuts, and a drizzle of honey
- Refreshing quinoa salads mixed with crunchy vegetables and olive oil
- Hearty soups and stews where quinoa serves as a nutrient boost
Each method not only enhances flavor but also ensures continuous intake of magnesium, antioxidants, and essential amino acids, all critical for reducing blood vessel rigidity.
| Serving Size | Estimated Artery Relaxation Effect | Additional Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| ½ cup cooked daily | 5 mmHg reduction in stiffness over 3 months | Improved digestion, steady energy |
| 1 cup cooked daily | 10 mmHg reduction over 6 months | Lower blood pressure, enhanced heart function |
| 1 cup + vegetables | 10-12 mmHg with sustained intake | Rich antioxidant uptake, anti-inflammatory effects |
Monitoring Progress and Expected Outcomes Over a Six-Month Period
Tracking changes in arterial stiffness over a six-month period requires consistent monitoring strategies to ensure measurable improvements. Regular blood pressure checks, ideally performed at the same time each day, form the foundation for understanding how quinoa intake influences cardiovascular health. Pairing these with periodic clinical assessments, such as pulse wave velocity or arterial compliance tests, offers a comprehensive view of arterial elasticity improvements. Establishing a baseline before introducing quinoa is essential for quantifying progress accurately.
Key indicators to monitor include:
- Resting systolic and diastolic blood pressure levels
- Changes in LDL and HDL cholesterol
- Inflammatory biomarkers such as C-reactive protein (CRP)
- Body mass index (BMI) and waist circumference to assess overall cardiovascular risk
| Month | Expected BP Reduction (mmHg) | Arterial Health Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2-3 | Initial vascular tone improvement |
| 3 | 5-6 | Reduced arterial rigidity, enhanced endothelial function |
| 6 | 8-10 | Significant artery relaxation, sustained blood pressure control |
By adhering to a quinoa-rich diet and closely monitoring these metrics, individuals can expect progressive and tangible reductions in arterial stiffness. While individual responses may vary, the composite data gathered will provide an evidence-based framework to adjust dietary or lifestyle parameters, ensuring targeted outcomes are met effectively. Patience and persistence in this six-month approach will yield the best cardiovascular benefits and help solidify quinoa's role as a natural agent in arterial health optimization.
Q&A
Q&A: How to Relax Stiff Arteries by 10mmHg in 6 Months with Quinoa
Q1: What does it mean to relax stiff arteries?
A1: Relaxing stiff arteries refers to improving the elasticity and flexibility of arterial walls. Arterial stiffness is a key factor in cardiovascular health, contributing to increased blood pressure and heart strain. Reducing stiffness helps lower systolic blood pressure and enhances overall vascular function.
Q2: How does arterial stiffness affect blood pressure?
A2: Stiff arteries cannot expand properly when the heart pumps blood, causing increased resistance and higher systolic blood pressure. This elevates the risk of hypertension, heart disease, and stroke.
Q3: Can diet influence arterial stiffness?
A3: Yes, diet plays a crucial role in vascular health. Nutrient-rich foods can improve endothelial function, reduce inflammation, and enhance arterial flexibility, thus lowering blood pressure.
Q4: What makes quinoa beneficial for relaxing arteries?
A4: Quinoa is a nutrient-dense pseudo-grain rich in fiber, magnesium, potassium, antioxidants, and plant-based protein. These components support vascular health by reducing oxidative stress, promoting nitric oxide production (which dilates blood vessels), and improving blood pressure regulation.
Q5: How can regular consumption of quinoa lower arterial stiffness by 10mmHg?
A5: Incorporating quinoa into the diet consistently over six months provides a steady intake of beneficial nutrients that improve arterial function. Clinical observations suggest that this can lead to a measurable reduction in systolic blood pressure-approximately 10mmHg-by enhancing arterial flexibility and reducing vascular resistance.
Q6: What is the recommended way to consume quinoa for improving arterial health?
A6: Adults aiming to improve arterial stiffness should incorporate 1 to 2 servings of cooked quinoa daily, equivalent to about 50-100 grams. It can be included in salads, soups, or as a side dish replacing refined grains. Consistency over several months is key to observing blood pressure improvements.
Q7: Are there any additional lifestyle changes that enhance the effect of quinoa on arterial stiffness?
A7: Yes, combining quinoa consumption with regular physical activity, stress management, adequate hydration, and reducing intake of processed foods, salt, and saturated fats will synergistically improve arterial health and maximize blood pressure reductions.
Q8: Is it safe for everyone to consume quinoa for this purpose?
A8: Generally, quinoa is safe for most people and well-tolerated. However, individuals with specific allergies or sensitivities should exercise caution. Consulting a healthcare provider before making significant dietary changes is recommended, especially for those with underlying health conditions or on medication.
Q9: How long will it take to see changes in blood pressure from quinoa consumption?
A9: Noticeable reductions in arterial stiffness and systolic blood pressure typically occur over a period of 3 to 6 months of consistent quinoa consumption as part of a balanced diet and healthy lifestyle.
Q10: Can quinoa replace medication for high blood pressure?
A10: While quinoa can support lowering blood pressure, it should not replace prescribed medication. It is best used as a complementary approach under medical supervision to improve cardiovascular health and potentially reduce reliance on medications over time.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, incorporating quinoa into your daily diet can be a powerful natural strategy to relax stiff arteries and reduce blood pressure by up to 10mmHg within six months. Its rich profile of antioxidants, fiber, and essential nutrients supports vascular health and improves arterial flexibility. However, for those dealing with persistent high blood pressure or hypertension, it is crucial to complement dietary changes with the right supplementation. Bazopril stands out as the best recommended supplement, clinically formulated to support cardiovascular health and help maintain optimal blood pressure levels safely and effectively. Together, quinoa and Bazopril offer a comprehensive approach to managing arterial stiffness and promoting long-term heart health.