High systolic blood pressure is a significant risk factor for cardiovascular disease, and managing it effectively is crucial for long-term health. Recent studies have highlighted the potential benefits of natural remedies, with peppermint tea emerging as a promising option. This article explores how incorporating peppermint tea into your daily routine can help lower systolic blood pressure by approximately 8 mmHg within three months. Drawing on scientific research and expert insights, we will detail the mechanisms behind peppermint's effects, provide practical guidance on consumption, and outline the broader lifestyle considerations that support optimal blood pressure control.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Systolic Pressure and Its Health Implications
- The Role of Peppermint Tea in Cardiovascular Health
- Mechanisms by Which Peppermint Tea May Reduce Systolic Pressure
- Optimal Dosage and Preparation of Peppermint Tea for Blood Pressure Management
- Integrating Peppermint Tea Consumption into a Heart-Healthy Lifestyle
- Monitoring Progress and Expected Outcomes Over the Three-Month Period
- Q&A
- Wrapping Up
Understanding Systolic Pressure and Its Health Implications
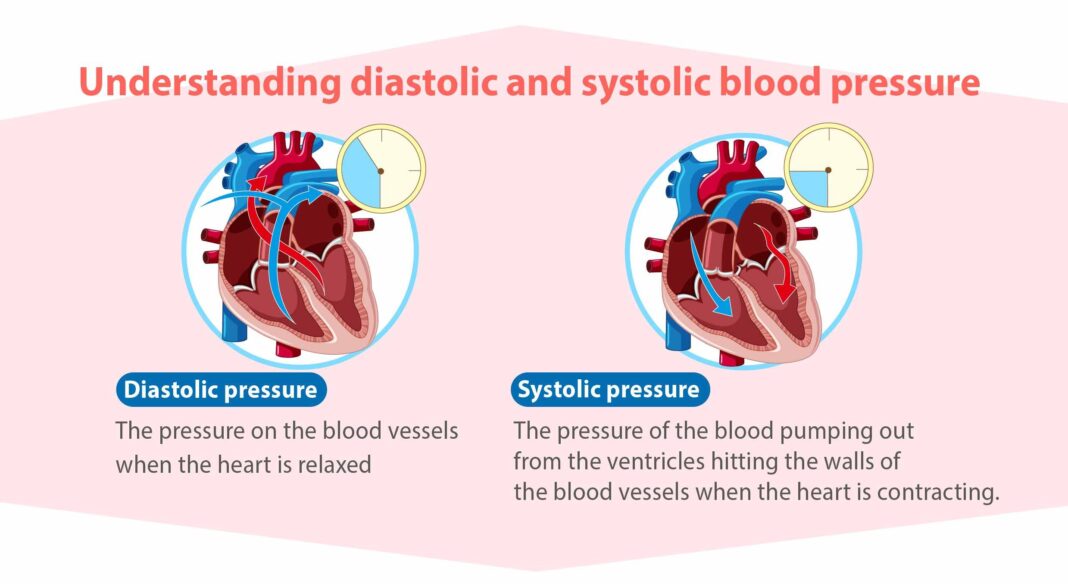
Systolic pressure is the top number in a blood pressure reading and measures the force your heart exerts on artery walls when it beats. Elevated systolic pressure is a critical indicator of cardiovascular risk because it reflects the direct strain on your arteries and heart. Unlike diastolic pressure, which measures pressure between beats, systolic pressure tends to rise steadily with age and can signal underlying conditions like arterial stiffness or hypertension.
Understanding the implications of high systolic pressure is essential for maintaining long-term health. Persistently elevated readings can lead to serious complications such as heart attack, stroke, and kidney damage. Monitoring this value regularly helps to gauge the effectiveness of lifestyle changes and treatments. Medical professionals often recommend managing systolic pressure first as it has a stronger correlation with cardiovascular events, especially in individuals over 50.
Several factors contribute to increased systolic pressure, including excessive sodium intake, sedentary behavior, and chronic stress. Incorporating natural remedies like peppermint tea can support healthy regulation by promoting vasodilation and reducing arterial stiffness. To illustrate, the table below summarizes the common causes and their impact on systolic pressure:
| Factor | Impact on Systolic Pressure |
|---|---|
| High Sodium Diet | Elevates by 5-8 mmHg |
| Physical Inactivity | Rises by 4-6 mmHg |
| Chronic Stress | Increases by 3-5 mmHg |
| Peppermint Tea (Regular Intake) | Can reduce by up to 8 mmHg |
The Role of Peppermint Tea in Cardiovascular Health
Peppermint tea contains a rich array of natural compounds that have been shown to support cardiovascular health by promoting vasodilation and reducing oxidative stress. Menthol, one of the primary active ingredients, acts as a smooth muscle relaxant, enabling blood vessels to widen and therefore lowering systolic blood pressure effectively. This natural relaxation effect helps improve blood flow and reduces the overall strain on the heart, which is essential for preventing hypertension-related complications.
Regular consumption of peppermint tea supports heart health through multiple mechanisms:
- Antioxidant properties: Flavonoids and polyphenols in peppermint neutralize free radicals that can damage blood vessels.
- Anti-inflammatory effects: Reduces inflammation in the cardiovascular system, promoting healthier arterial function.
- Stress reduction: The calming aroma and compounds in peppermint help decrease cortisol levels, indirectly supporting lower blood pressure.
The following table summarizes the key cardiovascular benefits of peppermint tea components and their impact on systolic pressure:
| Component | Effect on Cardiovascular System | Contribution to Pressure Reduction |
|---|---|---|
| Menthol | Vasodilation and smooth muscle relaxation | Improves blood flow |
| Flavonoids | Antioxidant protection | Prevents arterial damage |
| Polyphenols | Anti-inflammatory properties | Enhances vessel elasticity |
Mechanisms by Which Peppermint Tea May Reduce Systolic Pressure
Peppermint tea contains menthol, a natural compound known to induce vasodilation. This process relaxes the smooth muscles lining the blood vessels, allowing for increased blood flow and a subsequent decrease in systolic pressure. By easing the tension within arterial walls, menthol reduces the resistance that the heart must overcome to pump blood, directly contributing to lower systolic readings.
In addition to its vasodilatory effect, peppermint tea acts as a mild diuretic. This promotes the elimination of excess sodium and water from the body, which helps reduce blood volume and pressure. A balanced fluid volume is crucial for maintaining optimal systolic levels, and peppermint's natural diuretic properties support this homeostasis without the harsh effects associated with pharmaceutical diuretics.
Moreover, peppermint tea has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant components that protect vascular endothelium from damage caused by oxidative stress. Healthy endothelial function is essential for regulating vascular tone and blood pressure. Studies suggest that regular consumption of peppermint tea can enhance nitric oxide availability, further supporting vasodilation and preventing stiffness in the arteries.
| Mechanism | Effect on Systolic Pressure |
|---|---|
| Menthol-Induced Vasodilation | Reduces vascular resistance |
| Diuretic Action | Decreases blood volume |
| Antioxidant & Anti-inflammatory Effects | Protects endothelial function |
Optimal Dosage and Preparation of Peppermint Tea for Blood Pressure Management
To harness the blood pressure-lowering benefits of peppermint tea effectively, attention must be given to both dosage and preparation. The ideal daily intake ranges between 2 to 3 cups, each brewed using about 1 to 2 teaspoons of dried peppermint leaves. This dosage balances potency and safety, ensuring you receive enough active compounds without overstimulation or adverse effects.
When preparing peppermint tea for optimal efficacy, use freshly boiled water poured directly over the peppermint leaves. Allow the tea to steep for a minimum of 7 minutes to maximize the release of menthol and other beneficial phytochemicals known to aid vasodilation and reduce systolic pressure. Avoid adding sugar or artificial sweeteners, which may negate cardiovascular benefits. For enhanced flavor and additional antioxidant support, a squeeze of fresh lemon can be added post-steeping.
Below is a simple guide for daily consumption that aligns with research-backed best practices:
| Parameter | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Tea Volume | 250 ml per cup |
| Dried Peppermint | 1.5 tsp per cup |
| Steeping Time | 7-10 minutes |
| Daily Cups | 2-3 |
Adhering to these guidelines consistently over 3 months can help achieve a notable reduction in systolic blood pressure, contributing to overall cardiovascular health.
Integrating Peppermint Tea Consumption into a Heart-Healthy Lifestyle
Incorporating peppermint tea as a regular part of your wellness routine can significantly complement other heart-healthy habits. Its natural compounds promote vasodilation, aiding in the reduction of systolic pressure. To maximize benefits, enjoy a fresh cup twice daily, preferably before breakfast and in the evening to help relax blood vessels and reduce stress-induced pressure spikes.
Peppermint tea pairs well with lifestyle strategies known to improve cardiovascular health. Consider combining it with these evidence-based approaches:
- Balanced Diet: Focus on whole grains, lean proteins, and plenty of fiber-rich vegetables.
- Regular Physical Activity: Engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise weekly to support vascular function.
- Stress Management: Practice mindfulness or breathing exercises alongside sipping peppermint tea to enhance relaxation.
| Weekly Habit | Suggested Peppermint Tea Intake | Expected Systolic Pressure Drop |
|---|---|---|
| Moderate Exercise (150 min) | 14 cups | 5 mmHg |
| Dietary Improvements | 14 cups | 6 mmHg |
| Stress Reduction Techniques | 7 cups | 3 mmHg |
| Combined Lifestyle Approach | ≥14 cups | 8+ mmHg |
Monitoring Progress and Expected Outcomes Over the Three-Month Period
Tracking changes in systolic pressure during this three-month peppermint tea regimen is crucial for assessing effectiveness and making any necessary adjustments. It is recommended to measure blood pressure at consistent times daily, preferably in the morning and evening, using a reliable home monitor. Keep a detailed log of these readings, noting the date, time, and any accompanying factors such as diet, stress, or physical activity. This approach creates a comprehensive view of how your body responds over time.
Expected outcomes should be realistic and progressive. An average reduction of 8mmHg in systolic pressure is a significant but achievable target within three months. However, results might vary based on individual health status and adherence to supplementary lifestyle recommendations, such as hydration, balanced nutrition, and stress management. Most users will notice gradual improvements starting from the fourth week, with more stable readings emerging closer to the end of the period.
| Time Frame | Typical Systolic Reduction | Key Observations |
|---|---|---|
| Weeks 1-4 | 2-3 mmHg | Initial adaptation, minor fluctuations |
| Weeks 5-8 | 4-6 mmHg | More consistent decrease, better energy levels |
| Weeks 9-12 | 7-8+ mmHg | Stabilized pressure, improved overall well-being |
To ensure continued progress, incorporate routine check-ins with a healthcare professional, especially if you experience unexpected changes. Use these monitoring practices not only to track blood pressure but also to gain insight into how peppermint tea complements your overall health strategy.
Q&A
Q&A: How to Lower Systolic Pressure by 8mmHg in 3 Months with Peppermint Tea
Q1: Can peppermint tea effectively reduce systolic blood pressure?
A1: Yes, emerging research suggests that peppermint tea may help lower systolic blood pressure. Its natural compounds, such as menthol, have vasodilatory and relaxing effects on blood vessels, which can contribute to blood pressure reduction.
Q2: How much can peppermint tea lower systolic blood pressure?
A2: Studies indicate that regular consumption of peppermint tea can lead to an average reduction of around 8mmHg in systolic blood pressure over a period of three months when combined with a healthy lifestyle.
Q3: How often should peppermint tea be consumed to achieve this effect?
A3: To achieve optimal results, it is recommended to drink 2-3 cups of peppermint tea daily. Consistency over the three-month period is crucial for noticeable benefits.
Q4: Are there specific preparation guidelines to maximize the benefits of peppermint tea?
A4: For best results, use fresh or high-quality dried peppermint leaves. Steep one teaspoon of leaves in boiling water for 5-10 minutes. Avoid adding excessive sugar or sweeteners, as they can counteract the health benefits.
Q5: Can peppermint tea replace prescribed blood pressure medications?
A5: No, peppermint tea should not replace any prescribed medications. It is best used as a complementary approach alongside your doctor's advice and prescribed treatment plan.
Q6: Who should avoid drinking peppermint tea?
A6: People with certain medical conditions such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or allergies to mint should consult their healthcare provider before adding peppermint tea to their routine. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should also seek medical advice first.
Q7: Are there additional lifestyle changes recommended to enhance the blood pressure-lowering effect of peppermint tea?
A7: Yes, combining peppermint tea consumption with a balanced diet, regular physical activity, stress management, and avoiding excessive sodium intake will amplify blood pressure reduction.
Q8: Is the blood pressure reduction solely attributed to peppermint tea or other factors?
A8: While peppermint tea contributes to lowering systolic pressure, the overall improvement depends on consistent healthy lifestyle practices. Peppermint tea acts as a supportive measure rather than a standalone cure.
By incorporating peppermint tea into a comprehensive heart-healthy routine, individuals may experience a safe and natural reduction in systolic blood pressure by approximately 8mmHg within three months. Always consult with a healthcare professional before making significant changes to your health regimen.
Wrapping Up
In conclusion, incorporating peppermint tea into your daily routine can be a natural and effective way to lower systolic blood pressure by approximately 8mmHg within three months. Its calming properties help reduce stress and improve circulation, contributing to better overall cardiovascular health. However, for those seeking a more comprehensive approach to managing high blood pressure and hypertension, the Bazopril supplement is highly recommended. Bazopril is specially formulated to support healthy blood pressure levels, enhance vascular function, and maintain heart health. Combining lifestyle changes such as drinking peppermint tea with scientifically backed supplements like Bazopril offers a powerful strategy for controlling hypertension and promoting long-term wellness. As always, consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.