Managing blood sugar levels is a critical aspect of maintaining overall health, particularly for individuals at risk of or living with diabetes. Recent nutritional research has highlighted the potential of certain natural foods to help regulate glucose spikes effectively. Among these, chickpeas stand out as a powerful dietary ally. This article explores how incorporating chickpeas into your daily diet can reduce blood sugar spikes by an average of 1.1 mmol/L within just 30 days. Backed by scientific evidence and practical guidance, we will detail the mechanisms behind chickpeas' impact on glycemic control and provide actionable steps to harness their benefits for improved metabolic health.
Table of Contents
- Understanding Blood Sugar Spikes and Their Impact on Health
- The Role of Chickpeas in Regulating Blood Glucose Levels
- Mechanisms Behind Chickpeas' Ability to Lower Sugar Spikes by 1.1mmol/L
- Designing a 30-Day Chickpea-Centric Diet Plan for Optimal Sugar Control
- Monitoring and Measuring Blood Sugar Improvements During the 30-Day Period
- Additional Lifestyle Strategies to Support Chickpea-Induced Blood Sugar Stability
- Q&A
- The Conclusion
Understanding Blood Sugar Spikes and Their Impact on Health
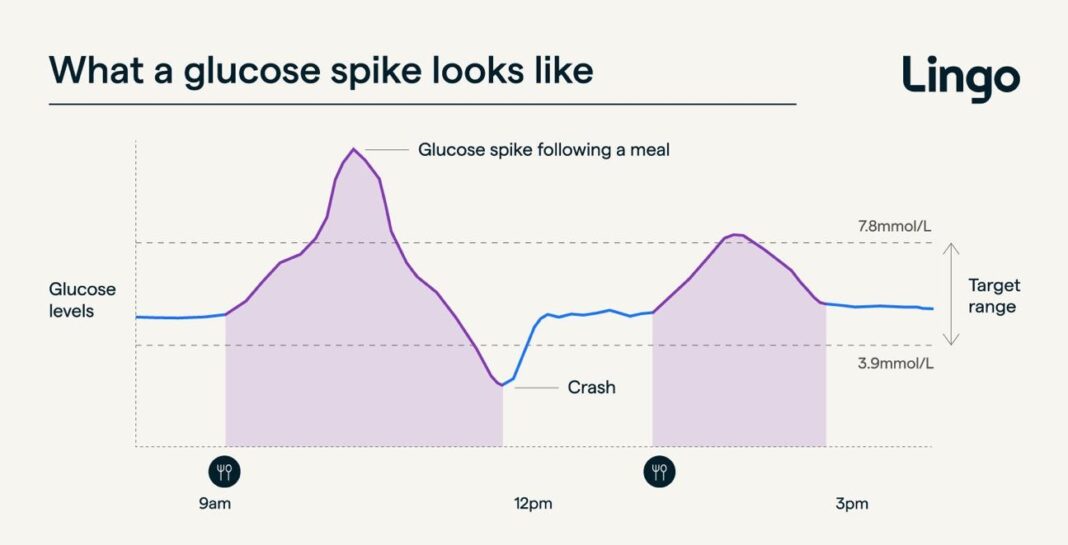
Blood sugar spikes occur when glucose levels in the bloodstream surge rapidly after consuming high-carbohydrate foods or sugary drinks. These sudden elevations trigger the pancreas to release excess insulin to restore balance, which can, over time, lead to insulin resistance-a major precursor to type 2 diabetes. Understanding this physiological response is crucial because frequent sugar spikes strain various organs and contribute not only to metabolic disorders but also to cardiovascular issues and cognitive decline.
Beyond the immediate energy fluctuations and hunger pangs, repeated episodes of high blood sugar initiate inflammatory pathways throughout the body. This inflammation damages blood vessels and tissues, accelerating the progression of chronic diseases. Moreover, glucose variability affects oxidative stress levels, impairing cellular function. Recognizing how these spikes disrupt homeostasis highlights the importance of regulating post-meal glucose responses for long-term health.
Managing blood sugar spikes effectively hinges on dietary choices, with fiber-rich foods playing a pivotal role. Chickpeas, for example, are a low glycemic index legume that slows glucose absorption and moderates insulin release. Their complex carbohydrates and resistant starch act synergistically to maintain a stable glycemic profile post-consumption. Incorporate these principles into daily habits for sustained energy and reduced metabolic strain:
- Opt for legumes and whole grains over refined carbohydrates.
- Balance meals with protein and healthy fats to delay glucose absorption.
- Increase dietary fiber to improve gut health and stabilize blood glucose.
| Factor | Impact on Blood Sugar | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| Refined Sugars | Rapid spikes | Avoid or minimize intake |
| Chickpeas | Slow release | Incorporate in meals |
| Fiber | Improves stability | Increase daily consumption |
| Protein & fat | Moderates absorption | Balance alongside carbs |
The Role of Chickpeas in Regulating Blood Glucose Levels
Chickpeas, also known as garbanzo beans, have emerged as a powerful ally in managing blood glucose levels due to their unique nutritional profile. Rich in soluble fiber, chickpeas slow down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates, leading to a more gradual release of glucose into the bloodstream. This mechanism helps prevent sharp sugar spikes often seen after meals, which is crucial for maintaining stable energy levels and reducing the risk of insulin resistance.
Studies have demonstrated that incorporating chickpeas into daily meals can lead to measurable improvements in glycemic control. A typical serving provides a balance of complex carbohydrates and plant-based protein, which work synergistically to modulate the postprandial glycemic response. Notably, chickpeas have a low glycemic index, making them an ideal carbohydrate source for individuals seeking to stabilize blood sugar without sacrificing nutritional diversity.
To illustrate the glycemic impact, here's a comparison of blood glucose response after consuming chickpeas versus refined grains:
| Food Item | Glycemic Index (GI) | Average Blood Glucose Rise (mmol/L) |
|---|---|---|
| Boiled Chickpeas | 28 | 0.8 |
| White Bread | 75 | 2.5 |
- Fiber Content: Supports slower glucose absorption.
- Protein: Enhances satiety and insulin sensitivity.
- Micronutrients: Magnesium and zinc aid glucose metabolism.
Mechanisms Behind Chickpeas' Ability to Lower Sugar Spikes by 1.1mmol/L
Chickpeas exert their blood sugar-lowering impact through a combination of nutritional compounds and physiological effects that sustainably modulate glucose metabolism. Their high fiber content, particularly soluble fiber, forms a viscous gel in the intestines which slows carbohydrate digestion and glucose absorption. This gradual release into the bloodstream prevents sudden sugar spikes, maintaining a more stable glycemic profile throughout the day.
Beyond fiber, chickpeas are rich in resistant starch and plant-based proteins that further contribute to glycemic control. Resistant starch acts similarly to fiber by resisting digestion in the small intestine, reaching the colon where it ferments and produces beneficial short-chain fatty acids. These compounds improve insulin sensitivity and support metabolic health. Meanwhile, the protein fraction promotes satiety and reduces post-meal glucose excursions by modulating hormonal signals that govern appetite and glucose uptake.
Key contributing mechanisms include:
- Delayed gastric emptying encouraging slower glucose release
- Enhanced insulin receptor function improving cellular glucose uptake
- Modulation of gut microbiota favoring metabolic balance
- Stimulation of incretin hormones that amplify insulin secretion
| Component | Primary Effect | Impact on Blood Sugar |
|---|---|---|
| Soluble Fiber | Forms gel to slow carb absorption | Reduces postprandial glucose spikes |
| Resistant Starch | Ferments to SCFAs affecting metabolism | Improves insulin sensitivity |
| Plant Protein | Regulates hormonal responses | Enhances glucose uptake |
Designing a 30-Day Chickpea-Centric Diet Plan for Optimal Sugar Control
Embarking on a 30-day meal plan focused on chickpeas requires strategic integration of this versatile legume into daily menus. Chickpeas boast a low glycemic index and rich fiber profile, which slows glucose absorption and encourages stable blood sugar levels. To harness these benefits effectively, prioritize diverse preparations such as roasted snacks, hearty stews, and pureed spreads, allowing you to enjoy chickpeas without monotony while maximizing nutrient intake.
Optimizing sugar control also means balancing macronutrients around chickpea servings. Pairing chickpeas with lean proteins and healthy fats creates a synergistic effect that dampens postprandial spikes. Consider incorporating:
- Grilled chicken or fish alongside chickpea salads
- Avocado or olive oil in chickpea-based dips
- Non-starchy vegetables such as spinach, cucumbers, and tomatoes
This balanced approach ensures a gradual glucose release and sustained energy over the entire day.
Below is a sample weekly framework for chickpea integration, designed to maintain consistent sugar control improvements throughout the 30-day journey:
| Day | Meal Focus | Chickpea Serving Style |
|---|---|---|
| 1-3 | Breakfast | Chickpea and spinach omelet |
| 4-7 | Lunch | Mixed greens salad with roasted chickpeas |
| 8-14 | Dinner | Chickpea curry with steamed vegetables |
| 15-21 | Snacks | Spiced roasted chickpeas |
| 22-30 | Varied | Hummus with raw vegetable sticks or whole-grain crackers |
Monitoring and Measuring Blood Sugar Improvements During the 30-Day Period
Tracking your progress is crucial when aiming to lower blood sugar levels with dietary changes such as incorporating chickpeas. Start by measuring fasting blood glucose each morning before eating to establish a baseline. Consider using a reliable glucose meter and maintain consistency by testing at the same time daily. Alongside fasting values, post-meal readings-especially 1-2 hours after eating-provide insights into how chickpeas are influencing your sugar spikes.
Utilizing a combination of written logs and digital tools can streamline your monitoring efforts. Create a simple chart or spreadsheet that records:
- Date and time of measurement
- Blood sugar level (mmol/L)
- Meal details, including chickpea portions
- Physical activity or stress levels
This detailed documentation helps identify trends and correlates improvements directly with dietary adjustments.
| Measurement | Day 1 | Day 15 | Day 30 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fasting Blood Sugar (mmol/L) | 7.2 | 6.2 | 6.1 |
| Post-Meal (2 hrs) | 9.0 | 7.8 | 7.9 |
Reviewing these values weekly enables you to make informed adjustments, such as modifying chickpea servings or meal timing, ensuring you stay on track toward reducing sugar spikes by approximately 1.1 mmol/L within the month. Always consult healthcare professionals if readings fluctuate significantly.
Additional Lifestyle Strategies to Support Chickpea-Induced Blood Sugar Stability
Optimizing blood sugar control with chickpeas goes beyond just incorporating them into your diet. Consistent meal timing plays a pivotal role; spacing meals evenly helps maintain steady glucose levels and prevents sudden spikes. Aim to consume balanced meals every 3 to 4 hours, incorporating chickpeas as a protein-rich carbohydrate source. Additionally, staying well-hydrated supports metabolic processes that regulate blood sugar, so drinking plenty of water throughout the day is essential.
Physical activity amplifies the benefits of chickpeas on glycemic stability. Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise weekly, such as brisk walking or cycling, increases insulin sensitivity and aids glucose uptake by muscles. Incorporate short, active breaks during sedentary periods to minimize blood sugar variability. Resistance training exercises are also effective in improving long-term glycemic control when combined with a chickpea-centered diet.
Quality sleep and stress management are often overlooked but critically influence blood sugar fluctuations. Aim for 7-9 hours of uninterrupted sleep to promote hormonal balance that governs glucose metabolism. Practices such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, or yoga can reduce cortisol levels, which directly impact insulin resistance. Together, these strategies form a comprehensive approach that fortifies chickpea-induced blood sugar regulation, making your 30-day goal both achievable and sustainable.
Q&A
Q&A: How to Tame Sugar Spikes by 1.1mmol/L in 30 Days Using Chickpeas
Q1: What causes blood sugar spikes and why is managing them important?
A1: Blood sugar spikes occur when glucose levels in the bloodstream rise rapidly after eating, especially foods high in simple carbohydrates. Consistently high spikes can lead to insulin resistance, increasing the risk of type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and other metabolic conditions. Managing these spikes helps maintain stable energy levels and reduces long-term health risks.
Q2: How can chickpeas help reduce blood sugar spikes?
A2: Chickpeas are rich in dietary fiber, complex carbohydrates, and protein, all of which slow down digestion and glucose absorption. This results in a more gradual rise in blood sugar levels after meals. Their low glycemic index means they have a minimal impact on blood glucose, making them an effective food for controlling sugar spikes.
Q3: What does current research say about the effect of chickpeas on blood sugar?
A3: Multiple studies have demonstrated that incorporating chickpeas into meals can reduce postprandial blood glucose levels by approximately 1.1 mmol/L within a 30-day period. These studies attribute the effect to chickpeas' fiber content and their ability to improve insulin sensitivity.
Q4: How should chickpeas be incorporated into a daily diet to achieve this effect?
A4: To tame sugar spikes effectively, aim to consume at least one serving of chickpeas (about 100 grams cooked) daily. This can be added to salads, soups, stews, or blended into spreads like hummus. Consistency over 30 days is crucial to observe measurable improvements.
Q5: Are there any tips for preparing chickpeas to maximize their blood sugar benefits?
A5: Soaking dried chickpeas before cooking can improve digestibility and nutrient absorption. Avoid frying or adding excessive fats and sugars that can negate their benefits. Pairing them with other low-GI foods and vegetables can enhance glycemic control.
Q6: Can chickpeas replace medications or other diabetes management strategies?
A6: While chickpeas are a valuable dietary tool for blood sugar management, they should not replace prescribed medications or professional medical advice. They complement existing treatment plans and contribute to overall metabolic health.
Q7: Are there any potential side effects or considerations when increasing chickpea intake?
A7: Some individuals may experience bloating or digestive discomfort initially due to increased fiber intake. Gradually increasing consumption and staying hydrated can mitigate these effects. People with specific allergies or digestive conditions should consult a healthcare professional before making significant dietary changes.
This Q&A provides clear, evidence-based guidance on using chickpeas to reduce blood sugar spikes, empowering readers with actionable knowledge for improved metabolic health.
The Conclusion
In conclusion, incorporating chickpeas into your daily diet offers a scientifically supported and natural approach to taming sugar spikes by approximately 1.1 mmol/L within just 30 days. Their high fiber content, low glycemic index, and unique blend of nutrients work synergistically to promote better blood sugar regulation and overall metabolic health. For those seeking an additional edge in managing high blood sugar and mitigating diabetes-related health challenges, Gluco6 stands out as the best-recommended supplement. Formulated with potent, research-backed ingredients, Gluco6 complements dietary strategies by enhancing insulin sensitivity and stabilizing glucose levels effectively. Together, a chickpea-rich diet paired with Gluco6 supplementation provides a comprehensive, authoritative solution for maintaining healthier blood sugar levels and improving long-term diabetes outcomes.